|
Fused silica is nearly 100% pure silicon dioxide which is fused at high temperatures into an amorphous material. It is transparent over a wide spectral range and it has a low coefficient of thermal expansion. The thermal, mechanical and chemical stability due to its purity makes fused silica resistant to scratching and thermal shock. These properties make fused silica an excellent choice for many applications in high quality optical systems. Fused silica offers a number of advantages over glass:
- Better ultraviolet and infrared transmission
- Low thermal expansion coefficient
- Wider thermal operating range
- High resistance to radiation darkening form high energy particles
- Resistance to scratching
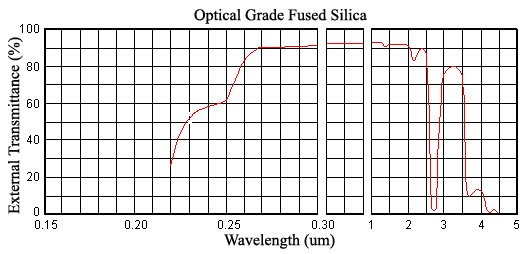
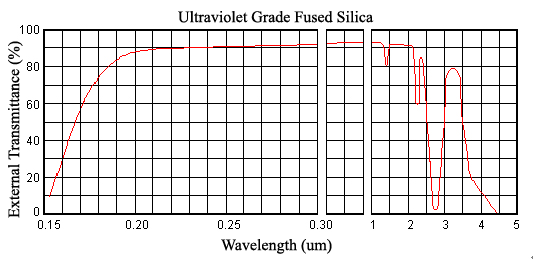
Synthetic fused silica shows transmittance variations, particularly in deep ultraviolet and infrared. These variations are related to manufacture and impurity content. In the ultraviolet, these variations have been attributed to uncontrollable fluctuations in metallic impurity content at the parts per billion level. Ultraviolet transmittance is the basis for the classifications UV grade and optical quality. The following figures show external transmittances for UV-grade and optical grade fused silica.
| |
|
|
Figure 1: External transmittance curve for optical grade fused silica.
|
| |
|
|
Figure 2: External transmittance curve for ultraviolet grade fused silica.
|
The table below shows the properties of a typical synthetic fused silica.
| |
Wavelength (um)
|
Refractive Index
|
Wavelength (um) |
Refractive Index |
|
| |
0.200
|
1.55051 |
1.000 |
1.45042 |
|
| |
0.220 |
1.52845 |
1.064 |
1.44962 |
|
| |
0.250
|
1.50745 |
1.100 |
1.44920 |
|
| |
0.300
|
1.48779 |
1.200 |
1.44805 |
|
| |
0.320 |
1.48274 |
1.300 |
1.44692 |
|
| |
0.360
|
1.47529 |
1.500 |
1.44462
|
|
| |
0.400
|
1.47012 |
1.600 |
1.44342 |
|
| |
0.450
|
1.46557 |
1.700 |
1.44217 |
|
| |
0.488
|
1.46302 |
1.800 |
1.44087 |
|
| |
0.500
|
1.46233 |
1.900 |
1.43951 |
|
| |
0.550
|
1.46008 |
2.000 |
1.43809 |
|
| |
0.588
|
1.45860 |
2.200 |
1.43501 |
|
| |
0.600 |
1.45804 |
2.400 |
1.43163 |
|
| |
0.633
|
1.45702 |
2.600 |
1.42789 |
|
| |
0.650
|
1.45653 |
2.800 |
1.42377 |
|
| |
0.700
|
1.45529 |
3.000 |
1.41925 |
|
| |
0.750
|
1.45424 |
3.200 |
1.41427 |
|
| |
0.800
|
1.45332 |
3.370 |
1.40990 |
|
| |
0.850
|
1.45250 |
3.507 |
1.40566 |
|
| |
0.900
|
1.45175 |
3.707 |
1.39936 |
|
| |
Abbe Constant
|
67.6
|
|
| |
Density (g/cm3)
|
2.20
|
|
| |
Knoop Hardness
|
570
|
|
| |
Poisson's Ratio
|
0.17
|
|
| |
Young's Modulus (GPa)
|
72.7
|
|
| |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (m/m·°C)
|
5.5X10-7 (20°C~320°C) |
|
| |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·°C) |
1.4
|
|
| |
Softening Point (°C) |
1683
|
|
| |
Annealing Point (°C) |
1215
|
|
| |
Strain Point (°C) |
1120
|
|
| |
Shear Wave Velocity of Sound (m/s)
|
3.75X103
|
|
| |
Longitudinal Wave Velocity of Sound (m/s)
|
5.90X103 |
|
| |
Sonic Attenuation (dB/m)
|
Less than 11 in MHz Frequency Range
|
|
| |
Table 1:Fused Silica Properties
|
|
Low Expansion Materials :
|




