|
Lithium Niobate, a well-developed optical material, has been widely used for surfaced acoustic devices, integrated optic devices, and new wavelength generation and refractive elements. The wide applications are due to its fundamental properties including high electro-optic and nonlinear optic coefficients, a wide transparency range, high electro-mechanical coupling coefficients, and excellent chemical and mechanical stability.
| |
|
| |
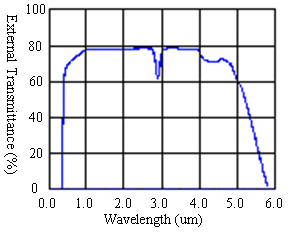
Figure 1: External transmittance curve for lithium niobate crystal
|
| |
Crystal Structure |
Trigonal
|
|
| |
lattice constant (Å) |
a = 5.148, c = 13.863
|
|
| |
Melting Point (°C) |
1255 ± 5
|
|
| |
Curie Point (°C) |
1140 ± 5 |
|
| |
Mohs Hardness |
5
|
|
| |
Density (g/cm^3) |
4.64
|
|
| |
Absorption Coefficient (/cm) |
α<0.001 at 1064nm
|
| |
Hygroscopic Susceptibility |
No
|
|
| |
Relative Dielectric Constant |
εT11 /εo= 85, εT33 /εo= 29.5 |
| |
Linear Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (25°C) ( /°C)
|
||C: 7.5X10-6
⊥C: 15X10-6 |
|
| |
Optical Homogeneity (/cm) |
≈ 5×10-5
|
|
| |
Transmission Range (nm) |
420 ~ 5200
|
|
| |
Damage Threshold (MW/cm2)
|
100 at 1064nm (10ns) |
|
| |
Refractive Indices |
no = 2.220, ne = 2.146 at 1300 nm
no = 2.232, ne = 2.156 at 1064nm
no = 2.268, ne = 2.203 at 632.8nm
|
|
| |
Sellmeier Equations (λ in um)
|
no2 = 4.9048+0.11768/(λ2-0.04750)-0.027169×λ2
ne2 = 4.5820+0.099169/(λ2-0.04443)-0.021950×λ2
|
|
| |
Nonlinear Optical Coefficients (pm/V)
|
d33=34.4, d31=d15=5.95, d22=3.07
|
|
| |
Electro-optic Coefficients (pm/V at 633nm)
|
r33 = 32, r13 = 10, r22 = 6.8, r51=32 (low frequency)
r33 = 31, r13 = 8.6, r22 = 3.4, r51=28 (high frequency)
|
|
| |
Table 1: LiNbO3 Properties
|
|
|



